
Eliza Lorsan
About The Author
In 2016, Eliza received her Master’s degree in cultural studies and history. As a student, she gave lectures at local cultural centers. She has been interested in coin collecting since she read the article about the historical importance of ancient numismatic items.
Since then Eliza has built her own collection, and later she also wrote her own articles on such topic. She knows that researching the steel 1943 wheat penny value is a crucial step for everyone ready to buy or sell these historic coins.
She has an online blog where subscribers can learn about the unique features of each coin depending on its country of origin. She continues giving the lectures and explaining to beginners what to pay attention to when collecting tokens.
Connect with Eliza



Wartime Relic
Among the huge number of collectible coins, some pieces have special value and importance in world history. This is not just currency; it is a physical reminder of our past economy, because the coin’s size and content are directly linked to the events happening at the time. This 1943 steel token is no exception.
Why Are 1943 Pennies Made of Steel?
The steel wheat penny value 1943 is a common search term for hobbyists interested in wartime coinage. In 1943 the US Mint found a different way to make pennies. They decided to stop using 95% copper for pennies and switch to something else: steel with a thin layer of zinc on top. This made the pennies look silvery-gray instead of their usual reddish-brown.
Even during the war, pennies were made in different parts of the United States. Each place had its own special mark to show where the coin came from.
- A steel 1C with no mint mark on it was made in Philadelphia. The mint in Philadelphia made around 684,628,670 of these coins
- A small letter “D” on the 1C means it was made in Denver. The mint in Denver made 217,660,000
- And if there is a little letter “S” – 1C came from San Francisco. The mint in San Francisco made 191,550,000
How Much Is a 1943 Steel Penny Worth? (2024 Prices)
Most 1943 steel pennies you might find today have been used a lot. If your 1943 steel penny is worn from use, it is often worth between 10 cents and 50 cents. This is just a bit more than its original value.
However, some 1943 pennies are very special and can be worth much more. This depends on their grade and if they have any rare mistakes from when they were made. A 1943 steel wheat penny value chart provides a quick reference for assessing prices based on mint mark.
| Name | Approximate Price Range |
| 1943 (Philadelphia – No Mint Mark) | $0.10 – $15 |
| 1943-D (Denver Mint Mark) | $0.15 – $20 |
| 1943-S (San Francisco Mint Mark) | $0.20 – $30 |
| 1943-D/D RPM (Repunched Mint Mark) | $100 – $10,000+ |
| 1943 Copper Cent | $100,000 – $1,000,000+ |
| 1944 Steel Cent | $75,000 – $400,000+ |
The 1943 steel wheat penny value no mint mark is approximate and may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors.
1943 (Philadelphia – No Mint Mark)
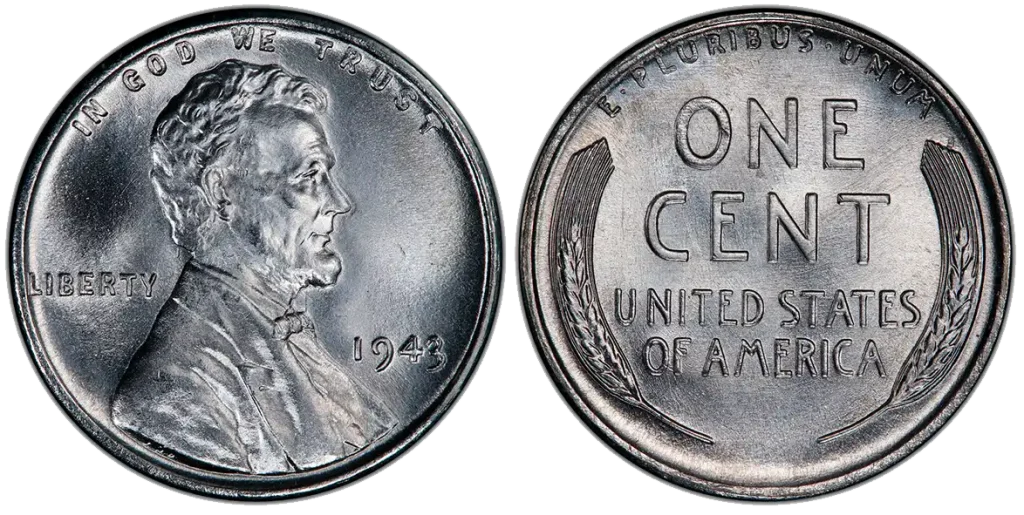
The 1943 steel lincoln wheat penny value is influenced by its unique composition during a pivotal moment in history.
- Mintage: 684,628,670
- Weight: 2.70 grams
- Diameter: 19.05 mm
1943-D (Denver Mint Mark)

The 1943 D wheat penny value steel is often slightly higher than the Philadelphia mint due to lower mintage.
- Mintage: 217,660,000
- Weight: 2.70 grams
- Diameter: 19.05 mm
1943-S (San Francisco Mint Mark)

The 1943 steel wheat penny S mint mark value is typically the highest among the standard steel cents due to its lower mintage.
- Mintage: 191,550,000
- Weight: 2.70 grams
- Diameter: 19.05 mm
1943-D/D RPM (Repunched Mint Mark)

- Mintage: This is an error variation within the 1943-D mintage (217,660,000). The exact number of RPM examples is unknown.
- Weight: 2.70 grams
- Diameter: 19.05 mm
1943 Copper Cent

- Mintage: Fewer than 20 known examples
- Weight: 3.11 grams
- Diameter: 19.05 mm
1944 Steel Cent
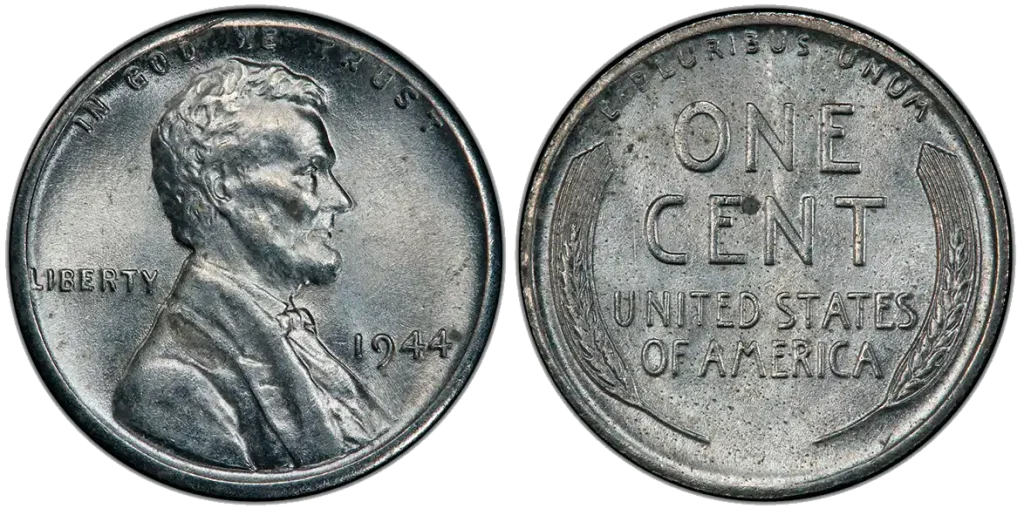
Investors often assess the potential worth of 1944 and value 1943 steel wheat penny as part of their numismatic portfolio.
- Mintage: Fewer than 10 known examples.
- Weight: 2.70 grams
- Diameter: 19.05 mm
Rare & Valuable 1943 Penny Mistakes (Errors)
Some 1943 pennies were made with rare mistakes. These are the ones that collectors hope to find. Their value can be much higher depending on the type of error and the condition.
The Super Rare 1943 Copper Cent
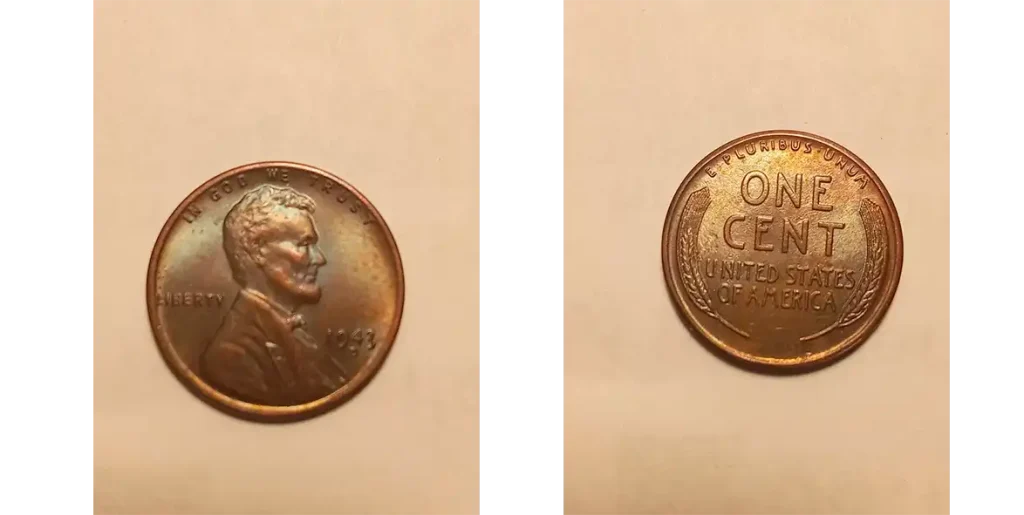

This is a very famous coin. Because the mint was changing to steel, a very, very small number of pennies were accidentally made using the old copper material in 1943.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| Good (G-4) to Fine (F-12) | $100,000 – $150,000 |
| Very Fine (VF-20) to Extremely Fine (XF-40) | $150,000 – $300,000 |
| About Uncirculated (AU-50 to AU-58) | $300,000 – $500,000 |
| Uncirculated (MS-60 to MS-63) | $500,000 – $800,000 |
| Uncirculated (MS-65 and up) | $800,000 – $1 Million+ |
The 1943 wheat penny value steel is approximate and may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors.
1943-D Repunched Mint Mark (RPM)
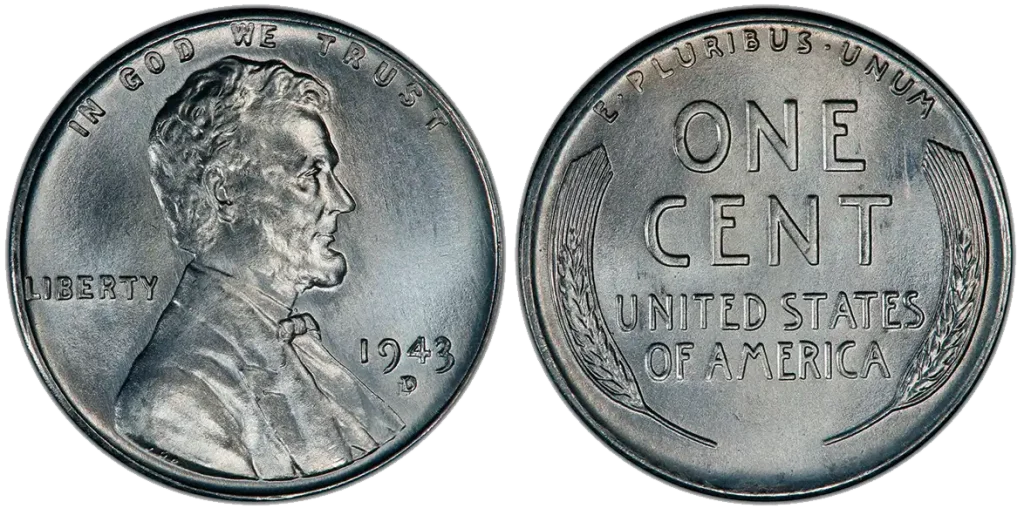
Sometimes, the machine that stamped the “D” hit the coin more than once, or it moved a little. This made the “D” look slightly doubled or unclear. The 1943 d steel wheat penny value today reflects its condition and errors.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| Fine (F-12) to Very Fine (VF-20) | $50 – $150 |
| Extremely Fine (XF-40) | $150 – $300 |
| About Uncirculated (AU-50) | $300 – $500 |
| Uncirculated (MS-60+) | $500 – $2,000+ |
The steel wheat penny 1943 value is approximate and may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors.
1943 Off-Center Strike
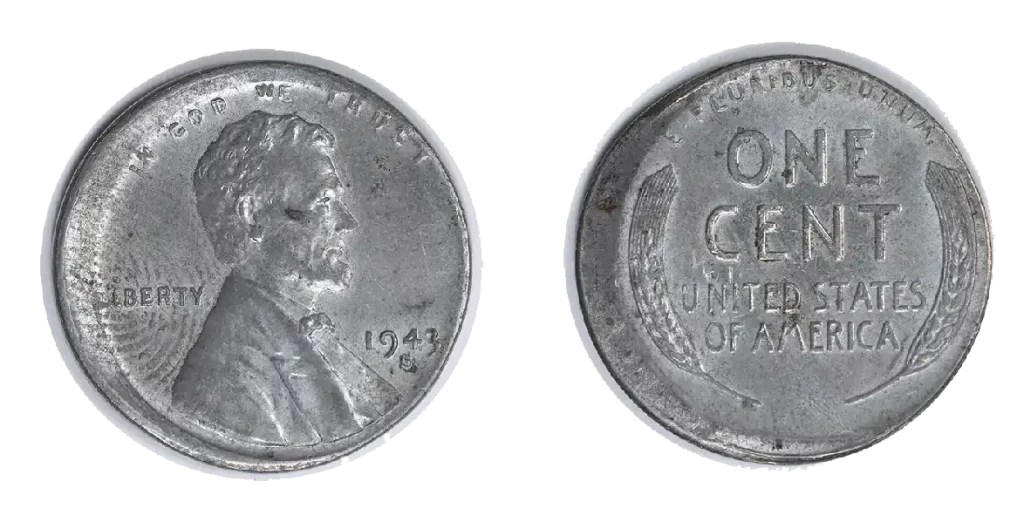
The 1943 steel wheat penny D mint mark value is generally higher with errors. An off-center strike happens when the coin is not perfectly in place when it is stamped. This means some part of the design might be missing, or the picture on the coin looks like it is sliding off the edge. Such error on the 1943-S is very rare.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| Fine (F-12) (Slightly Off) | $20 – $50 |
| Very Fine (VF-20) (Noticeably Off) | $50 – $150 |
| Extremely Fine (XF-40) (Major Off) | $150 – $300+ |
| Uncirculated (MS-60+) (Major Off) | $300 – $1,000+ |
The value of 1943 steel wheat penny is approximate and may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors.
1943 Double Die Obverse (DDO)

The 1943 P steel wheat penny value is usually the entry-level price for this specific year and type, but errors can increase the worth. A double die error means that the tool used to stamp the coin had a small mistake. This makes parts of the letters or numbers appear doubled.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| Fine (F-12) (Slight doubling) | $100 – $300 |
| Very Fine (VF-20) (Clear doubling) | $300 – $700 |
| Extremely Fine (XF-40) | $700 – $1,500 |
| Uncirculated (MS-60+) | $1,500 – $5,000+ |
The 1943 steel wheat penny no mint mark is approximate and may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors.
1943 Cent Cud Error

The 1943 S steel wheat penny value today represents one of the scarcer standard varieties especially with errors. A cud error happens when a part of the coin die breaks off.
The coin die is the metal stamp that presses the design onto the blank metal piece to make a coin. If a piece of this die breaks away, the missing part will show up as a raised, blank blob of metal on the coin.
| Grade | Approximate Value |
| Minor Cud | $20 – $80 |
| Clear Cud | $80 – $250 |
| Distinct Cud | $250 – $500 |
| Clear Cud | $500 – $1,000 |
| Large, clear Cud | $1,000 – $2,500+ |
The 1943 wheat steel penny value is approximate and may vary depending on the coin’s condition, market demand, and other factors.
How to Identify a Valuable 1943 Penny
Understanding the wheat penny 1943 steel value is essential for authenticating and pricing these wartime coins
Check the Metal
- Steel pennies are magnetic. Most 1943 pennies are made of steel with a zinc coating. This means they will stick to a magnet. You can easily test this with a small magnet, like one you use on your refrigerator. If your 1943 penny sticks to the magnet, it is a steel penny. These steel pennies have a silver-gray or dull gray color and weigh approximately 2.70 grams.
- Copper 1943 pennies are non-magnetic. These are the extremely rare ones. If you have a 1943 penny that doesn’t stick to a magnet, it is one of the few copper pennies that were accidentally made that year. These rare copper pennies have the reddish-brown color of a regular copper penny and weigh approximately 3.11 grams.
Look for Mistakes (Errors)
The wheat penny value 1943 steel depends significantly on its rare errors or high-grade characteristics.
- Repunched Mint Marks (RPMs): Sometimes the the small letter “D” or “S” was stamped more than once, or the stamping tool moved a little. This makes the mint mark look doubled or a bit blurry.
- Double Die Obverse (DDO): At the front of the coin you might see parts of words like “LIBERTY” or the date “1943” that look like they have a faint second image.
- Double Die Reverse (DDR): At the back of the coin you might see similar doubling on the words or numbers such as “ONE CENT” or “UNITED STATES OF AMERICA.”
- Off-Center Strikes: This happens when the coin was not perfectly in place when it was stamped. As a result, the design on the coin is not in the middle. Part of the design might be missing, and part of the coin’s edge might be empty or blank.
Grading Condition Matters
How good a coin looks is very important for its value.
- Circulated (G-VF): Most 1943 pennies you find will be circulated. This means they have been used as money and show signs of wear. For example, you can see parts of Lincoln’s cheek or hair are rubbed smooth. The more worn a coin is, the lower its grade will be.
Good (G): Very heavily worn, most details are flat, but the main features are still visible.
Fine (F): Moderate to considerable wear, but major designs are clear.
Very Fine (VF): Light to moderate wear on the high points of the design. All letters and main features are sharp.
- Uncirculated (MS-60+): An uncirculated coin is one that has never been used as money. It shows no signs of wear. It often has its original shine, called “luster.” These coins are usually worth much more than coins that have been used. The “MS” stands for “Mint State,” meaning it’s in the same condition as when it left the mint.
- Circulated (G-VF): Most 1943 pennies you find will be circulated. This means they have been used as money and show signs of wear. For example, you see the parts of Lincoln’s cheek or hair are rubbed smooth. The more worn a coin is, the lower its grade will be.
FAQ
Why is the 1943 copper penny so valuable?
The 1943 copper penny is so valuable because it was a mistake. During World War II, the United States government needed copper for war efforts, so they decided to make pennies from steel for that year. The few copper pennies that exist were made by accident, likely because some old copper coin material was still in the machines when the steel pennies started being produced.
How much is a 1943 steel penny with no mint mark worth?
A frequent question among new collectors is what is the value of a 1943 steel wheat penny? Most circulated 1943 steel pennies with no mint mark are worth between 10 cents and 50 cents. If the coin is in very good condition, it can be worth from $1 to $100 or more.
What’s the rarest 1943 penny?
The 1943 copper one is the rarest and most valuable 1943 penny. Only a handful of these coins are known to exist. Even a worn 1943 copper piece can be worth well over $100,000, and those in better condition can be worth much more.
Should I clean my 1943 steel penny?
No, you should never clean your 1943 steel cent, or any old coin for that matter. Cleaning a coin, even with gentle methods, can actually damage its surface. This damage can remove its original shine and natural look, which greatly lowers its value to coin collectors. A cleaned coin is almost always worth less than a dirty or toned coin in its original state. Determining the 1943 wheat penny steel value often requires careful examination for wear and tear.
How can I tell if my 1943 penny is steel or copper?
The easiest way is to test it with a magnet. A 1943 steel 1C will stick strongly to a magnet, while a copper penny will not. Additionally, steel pennies have a silver-gray appearance, whereas copper pennies are reddish-brown. For a more precise check, a copper one will also weigh about 3.11 grams, compared to the 2.70 grams of a steel.
Are there other valuable 1943 steel penny errors besides the copper one?
Yes, while the 1943 copper penny is the most famous error, other variations like the 1943-D/D Repunched Mint Mark (RPM) can also be valuable. Other less common errors, such as off-center strikes or die breaks, can also add value.
Why did they stop making steel pennies in 1944?
The steel cents were a temporary measure for wartime copper conservation. By 1944, the copper shortage had eased slightly, allowing the U.S. Mint to switch back to a bronze composition using recycled cartridge cases.
How should I store my 1943 steel penny?
Good options include Mylar flips, non-PVC coin holders, or certified coin slabs from professional grading services like PCGS or NGC. Avoid storing them in PVC flips, direct contact with cardboard that isn’t acid-free, or in environments with high humidity or extreme temperature fluctuations, as these can accelerate corrosion of the zinc coating. Remember that the 1943 steel wheat penny value today can fluctuate with market demand and the specific attributes.
In conclusion, within the huge amount of collectable coins, many people still are eager to know the 1943 steel penny wheat value. Created during World War II due to necessity, these unique coins are memorable pieces of American history. With these and many other tokens, we have the opportunity to connect with the past.